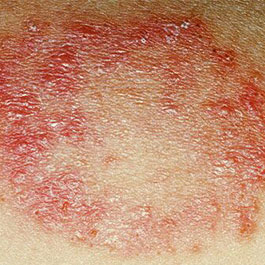
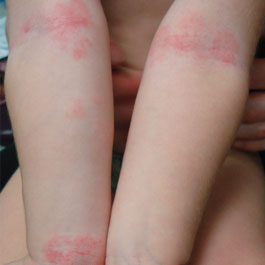
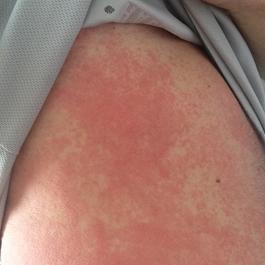
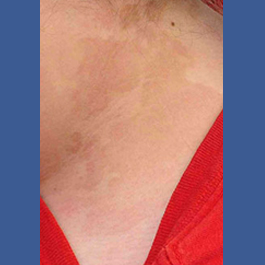
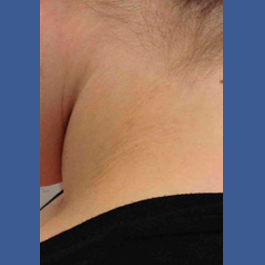
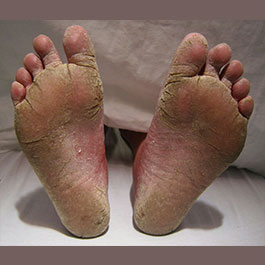
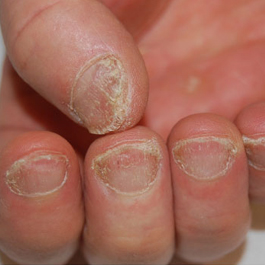
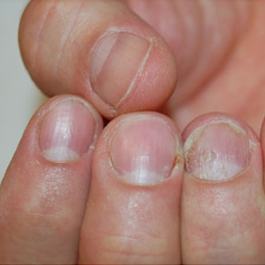
Fungal infections of the skin are very common and include athlete’s foot, jock itch, ringworm, and yeast infections.
Some fungi reproduce through tiny spores in the air. You can inhale the spores or they can land on you. As a result, fungal infections often start in the lungs or on the skin. You are more likely to get a fungal infection if you have a weakened immune system or take antibiotics.
Fungi can be difficult to kill. For skin and nail infections, you can apply medicine directly to the infected area. Oral antifungal medicines are also available for serious infections.
Fungi reproduce by spreading microscopic spores. These spores are often present in the air and soil, where they can be inhaled or come into contact with the surfaces of the body, primarily the skin. Consequently, fungal infections usually begin in the lungs or on the skin.
Of the wide variety of spores that land on the skin or are inhaled into the lungs, most types do not cause infection. A few types cause infection only in people who have one of the following:
:A weakened immune system
:Foreign material, including medical devices (such as an artificial joint or heart valve), in their body
The immune system may be weakened when people take drugs that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants), such as chemotherapy drugs or drugs used to prevent rejection of an organ transplant, or have a disorder such as AIDS.
Except for some superficial skin infections, fungal infections are rarely passed from one person to another.